Interface
The web-backend provides a GraphQL interface to communicate with it. GraphQL is a query language that provides type safe queries and mutations for the users to read and manipulate data. Additional information about GraphQL can be found here.
REST vs GraphQL
Nowadays, the two most popular way to communicate with backend APIs is REST and GraphQL. GraphQL is more recent and provides a lot of different advantages compared to REST. Probably the most important one is that it is type safe. In a REST API it's not possible to restrict a user to a body format. They can send any type of data they want and even REST helps with a lot of well working conventions it might still be confusing to the users what needs to be sent to the server and what type of data they can expect back. With GraphQL, it's a completely different story. The backend provides types and queries and the client is able to tell what they need.
Besides this major difference there's a lot of other concepts in which they differ. There's a lot of great articles about the comparison. e.g.: REST vs GraphQL.
The reason this technology has been chosen for this particular project is the maturity of the client side libraries. They provide out of the box caching and state management which is a great help in developing a good UI.
Authentication
The authentication happens with the help of JWT tokens. A token is sent in the redirection URL during the login process. There are a few exceptions, but generally this token has to be sent with every subsequent request in the Authorization header. The following format is required:
Authorization: Bearer <token>
Schema
The GraphQL schema can be written down using SDL(Schema Definition language). The following section contains all the available queries and mutations of the application with its description, relevant SDL part and a process diagram of the logic behind it.
Queries
Queries are requests that are meant to read data from the server. While it's technically possible, data should never be modified during the execution of a query. It's the GraphQL equivalent of a GET request.
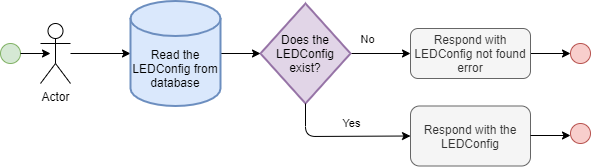
ledConfig
ledConfig(id: Int!): LEDConfig
type LEDConfig {
id: Int!
name: String!
configText: String!
createdAt: String!
viewCount: Int!
isFavorite: Boolean
tags: [Tag!]!
user: User!
}
ledConfigPage
This query is available without authentication
ledConfigPage(tags: [String], page: Int!, size: Int!, sort: SortMethod!): LEDConfigPage
type LEDConfigPage {
ledConfigs: [LEDConfig],
isLast: Boolean
}
enum SortMethod {
RECENT,
POPULAR
TOP_VOTED
}
Returns a collection of LEDConfigs based on the arguments.
- tags: The config has to be tagged with the specified tags
- sort: Sorts the LEDConfigs
- RECENT: sorted by creation date. The latest is the first
- POPULAR: sorted by view count. Most viewed is first.
- TOP_VOTED: sorted by vote count. Most voted is first.
The query supports pagination by accepting page and size arguments.
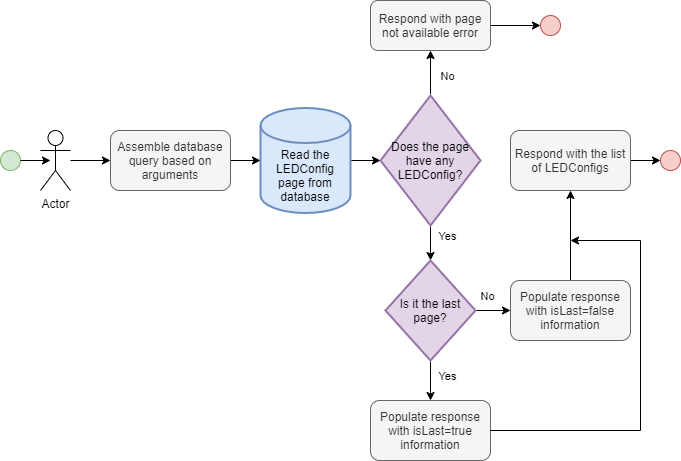
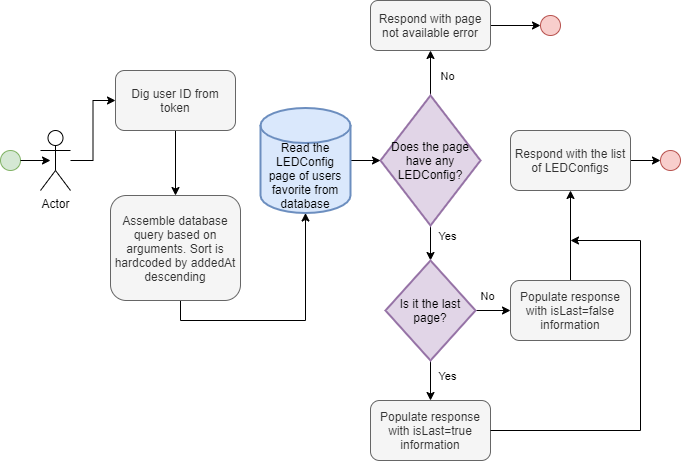
ledConfigFavoritesPage
ledConfigFavoritesPage(page: Int!, size: Int!): LEDConfigPage
Returns a collection of LEDConfigs that is favored by the user issuing the query
ledDeviceByMacAddress
ledDeviceByMacAddress(macAddress: String!): LEDDevice
type LEDDevice {
id: String
deviceId: String
macAddress: String
configuration: String
user: User
}
enum Status {
ONLINE
OFFLINE
}
Returns a LEDDevice with the given MAC address
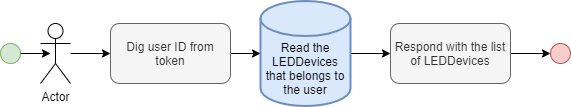
ledDevicesUser
ledDevicesUser: [LEDDevice]
Returns a collection of LEDDevices that belongs to the user issuing the query
tags
This query is available without authentication
tags: [Tag]
type Tag {
id: String
name: String
}
Returns all the existing tags

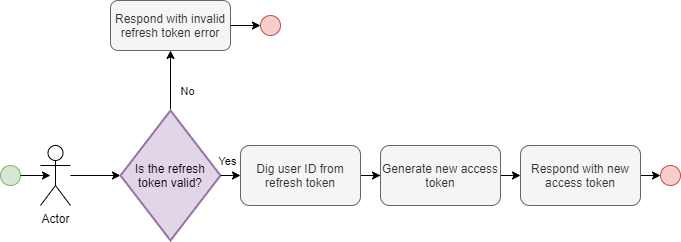
refreshToken
This query is available without authentication
refreshToken(refreshToken: String): String
Returns a new access token for the user. Expects a valid refresh token
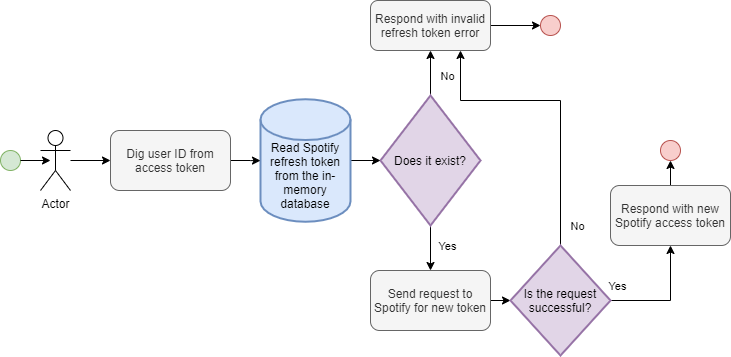
refreshSpotifyToken
refreshSpotifyToken: String
Returns a new spotify access token that belongs to the user issuing the query
Mutations
Mutations are requests that change the data on the server. They might create, update or delete data. There are no different ways of doing these actions like the HTTP methods. Mutations also respond with some kind of data.There are a few mutations in the application that always respond with a boolean true if no error happens. The reason for that is the response cannot be empty in GraphQL.
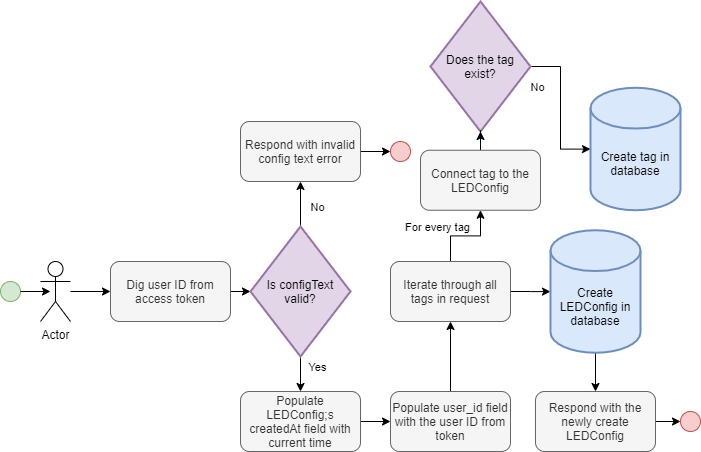
createLEDConfig
createLEDConfig(input: CreateLEDConfigInput!): LEDConfig
input CreateLEDConfigInput {
name: String!
configText: String!
hasMusicAction: Boolean!
tags: [String!]!
}
Creates a new LEDConfig in the database. It will belong to the user that issues the mutation. All the tags that don't exist are also created in the process. Returns the created LEDConfig.
deleteLEDConfig
deleteLEDConfig(input: DeleteLEDConfigInput!): Boolean!
input DeleteLEDConfigInput {
id: Int!
}
Deletes the LEDConfig with the given ID from the database.
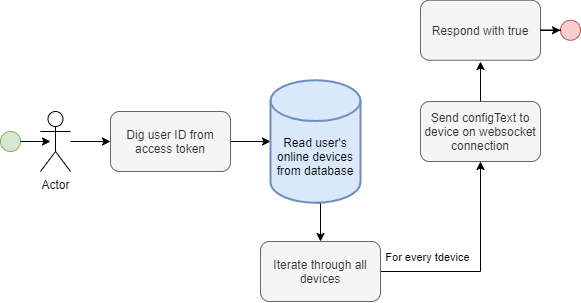
uploadLEDConfig
uploadLEDConfig(input: UploadLEDConfigInput!): Boolean!
input UploadLEDConfigInput {
configText: String
}
Sends a config to the online devices of the user that issues the mutation. Always returns true.
syncLEDConfig
syncLEDConfig: Boolean!
Starts music synchronization process on the user's devices. Always returns true.
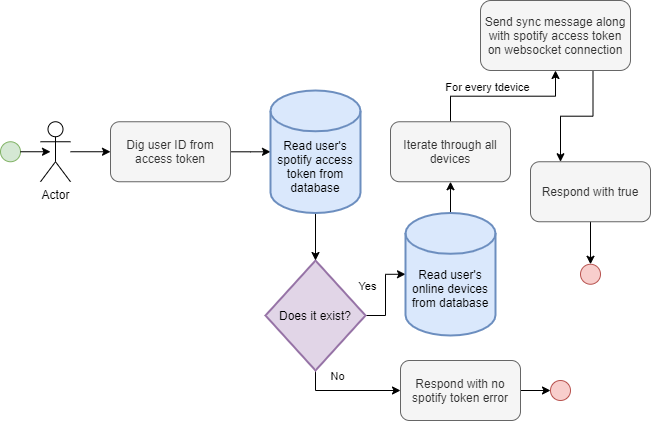
addToFavorites
addToFavorites(input: AddToFavoritesInput!): Boolean!
input AddToFavoritesInput {
ledConfigId: Int!
}
Adds a LEDConfig to the user's favorites. Returns true if the LEDConfig is already in the favorites, true otherwise.
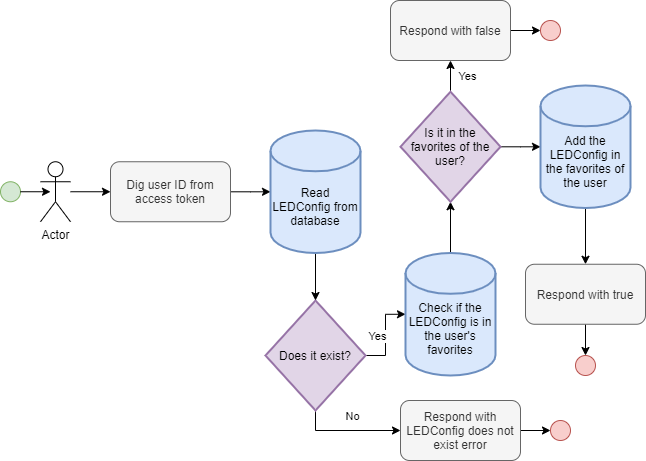
removeFromFavorites
removeFromFavorites(input: RemoveFromFavoritesInput!): Boolean!
input RemoveFromFavoritesInput {
ledConfigId: Int!
}
Removes a LEDConfig from the user's favorites. Returns true if the LEDConfig is is not in the favorites, true otherwise.
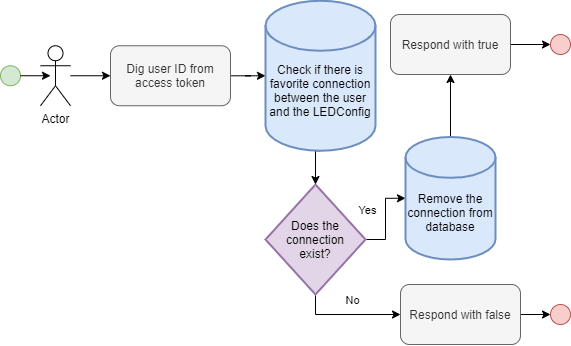
createLEDDevice
createLEDDevice(input: CreateLEDDeviceInput!): LEDDevice!
input CreateLEDDeviceInput {
deviceId: String
}
Creates a LEDDevice connected to the user that issues the mutation. Returns the created LEDDevice.
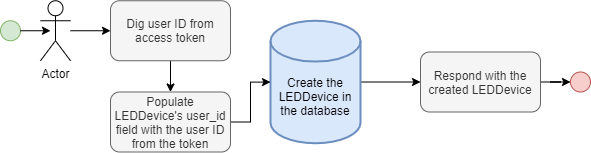
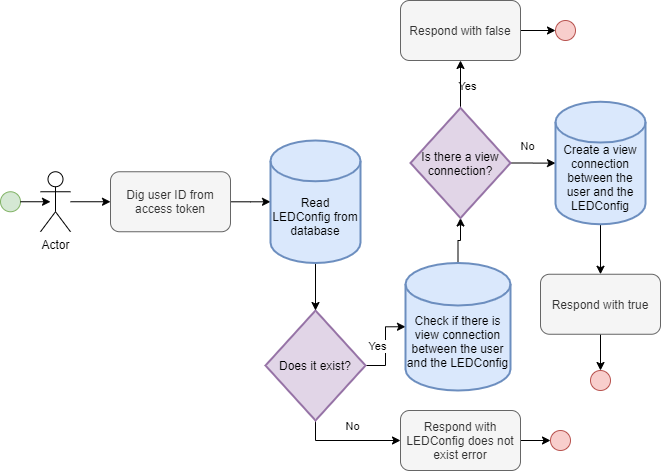
view
view(input: ViewInput!): Boolean!
input ViewInput {
ledConfigId: String
}
Registers a view connection between the LEDConfig in the argument and the user who issued the mutation. Returns false if the view connection already exists, true otherwise.
Error handling
During the execution of queries and mutation several different errors might
occur. In GraphQL the convention is that the response status should be 200 OK
and the response body should have an errors field that has additional
information about the error. The application follows this convention.
This is how an error looks like if the refreshToken query is called with an
invalid refresh token:
{
"errors": [
{
"message": "Exception while fetching data (/refreshToken) : Invalid
refresh token",
"locations": [
{
"line": 8,
"column": 3
}
],
"path": [
"refreshToken"
],
"extensions": {
"code": "UNAUTHENTICATED",
"classification": "DataFetchingException"
}
}
],
"data": {
"refreshToken": null
}
}
The nature of the error can be determined by the extensions > code field.
The following errors might occur:
- LEDConfig not found: There is no LEDConfig with the ID in the argument
- LEDConfig page does not exist: There is not enough LEDConfig in the query result to populate the given page
- Invalid access token: The access token sent in the request header does not exist or invalid
- Invalid refresh token: The refresh token provided is not valid