Security
Every data and functionality on the backend(except few) is only available for authenticated users.This authentication happens with JWT(JSON Web Token). The advantages of this technology is that it's scalable, modern, easy to implement and it fits this use case in every way. The way it works is that the user after logging in gets a token that is stored in the browser and this token is sent with every request towards the API. The backend is able to validate this token without any database operation and it tries to serve the request in case it is valid.
JWT
The JWT got its name from its format. The data is stored in JSON format. It is sent in encoded format which consists of 3 parts. Every part is separated with a dot character from each other.
Header
The header contains metadata. The information that it has to store no matter what is the hash algorithm that is used to create the signature. E.g.:
{
"alg": "HS512"
}
In the above example the hash algorithm is SHA-512.
Payload
The payload stores every non-meta information. By convention the information to
identify the user is stored in the sub(subject) field. It could be a username,
an ID generated by the database, etc. In this application the Spotify generated
ID can be found in this field. Also by convention the iat(issued at) and the
exp(expire) stores the information regarding the token expiration. In this
application a custom field is also stored called type. This field stores the
type of the token which might be ACCESS or REFRESH
{
"sub": "4i3xh4pmpsuau2k2mroyaxstz",
"iat": 1609347543,
"exp": 1609351143,
"type": "ACCESS"
}
Signature
The biggest disadvantage of these tokens is that if an attacker gets them they have unlimited access to the backend API on behalf of the user. Since the goal is to not make any database operation during the authentication adding these stolen tokens to a blacklist is not a good idea.
Hence the reason, these tokens have an expiration time property. This is a timestamp after the token can not be treated valid. It's a good practice to choose this time short(like 10-60 minutes). In this case the stolen tokens can not be used long enough to cause serious damage.
However this raises a new problem that the users have to reauthenticate too frequently. That is the reason why the two type of tokens exist. The access token can be used to communicate with the API. It has a short expiration time and there is no need to make database operation to validate it. On the other hand the refresh token has long expiration time(1-30 days), it can't be used to access resources and it can be blacklisted and therefore needs database operation for validity check. The refresh token can be used to request a new access token whenever that expires. As long as the refresh token is valid it can be used indefinitely to get new access tokens which means the user only has to authenticate when the refresh token expires.
This is how the validation of the access token looks like:
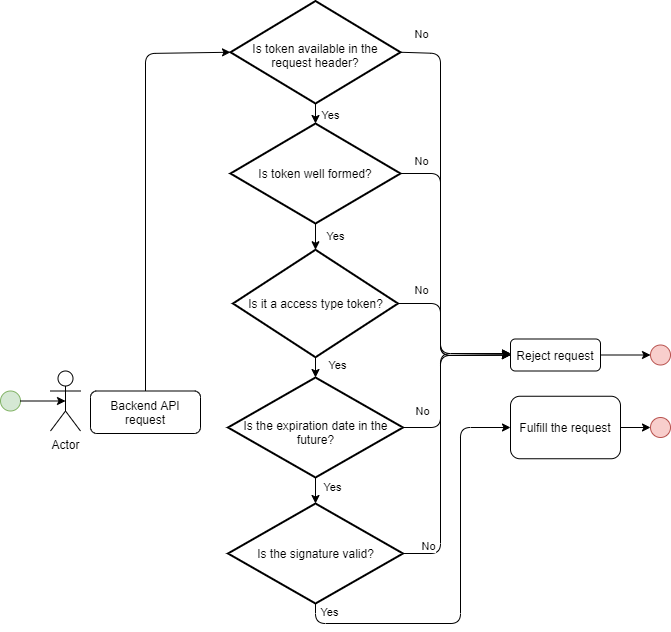
And this is how the refresh token validation looks like:
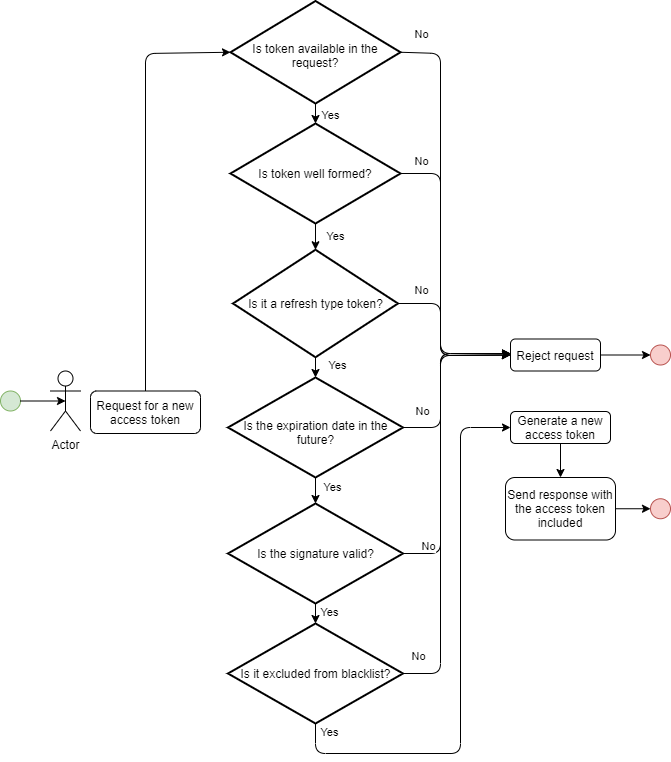
Note, that the blacklist check is the last in the process. This is a good practice to leave it the last step as this leaves the least chance of having to make it.